A contra account is an account with a balance opposite the normal accounts in its category. Contra accounts are usually linked to specific accounts on the balance sheet and are reported as subtractions from these accounts. In other words, contra accounts are used to reduce normal accounts on the balance sheet.
Prepaid Accounting: Everything You Need to Know
Each month, the company moves $1,000 from the prepaid expense account to the interest expense account as the interest is used. There are four key types of contra accounts—contra asset, contra liability, contra equity, and contra revenue. Contra assets decrease the balance of a fixed or capital asset, carrying a credit balance.
How Do You Record Accrued Expenses on a Balance Sheet?

Notice that the ending balance in the asset Supplies is now $725—the correct amount of supplies that the company actually has on hand. The income statement account Supplies Expense has been increased by the $375 adjusting entry. It is assumed that the decrease in the supplies on hand means that the supplies have been used during the current accounting period. The balance in Supplies Expense will increase during the year as the account is debited. Supplies Expense will start the next accounting year with a zero balance. The balance in the asset Supplies at the end of the accounting year will carry over to the next accounting year.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Account
Likewise, the net effect of the prepaid insurance journal entry in this example is zero on the balance sheet. This is due to one asset increases $1,200 and another asset decreases $1,200. Accounts receivable is rarely reported on the balance sheet at its net amount. Instead, it is reported at its full amount with an allowance for bad debts listed below it. Maybe more importantly, it shows investors and creditors what percentage of receivables the company is writing off.
When a specific account is identified as uncollectible, the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts should be debited and Accounts Receivable should be credited. Contra Equity Account – A contra equity account has a debit balance and decreases a standard equity account. Treasure stock is a good example as it carries a debit balance and decreases the overall stockholders’ equity. We’ve outlined the procedure for reporting prepaid expenses below in a little more detail, along with a few examples. The trial balance, drawn up on 31 December 2019, assumed that he had no other insurance and his insurance expenses account would show a balance of $4,800. The difference between an asset’s account balance and the contra account balance is known as the book value.
- There are two major methods of determining what should be booked into a contra account.
- In the business, the company usually needs to make an advance payment for the insurance that it has purchases.
- Prepaid assets are nonmonetary assets whose benefits affect more than one accounting period.
- Likewise, the net effect of the prepaid insurance journal entry in this example is zero on the balance sheet.
- Contra asset accounts are recorded with a credit balance that decreases the balance of an asset.
Related AccountingTools Courses
- This means that the debit balance in prepaid insurance on December 31 will be $2,000.
- And the company is usually required to pay an insurance fees for one year or more in advance.
- Prepaid insurance is insurance paid in advance and that has not yet expired on the date of the balance sheet.
- The key example of a contra equity account is Treasury stock, which represents the amount paid to buyback stock.
- This is usually done at the end of each accounting period through an adjusting entry.
- Treasure stock is a good example as it carries a debit balance and decreases the overall stockholders’ equity.
- However, after adjusting entry at the end of the period for the insurance expense, the asset account will decrease while the expense account will increase.
This requires proper calculation and amortization of prepaid expenditures such as insurance, software subscriptions, and leases. The most-common examples of prepaid expenses in accounting are prepaid rent from leases, prepaid software subscriptions, and prepaid insurance premiums. Below you’ll find a detailed description of each one as well as detailed accounting examples for each. Equipment is a noncurrent or long-term asset account which reports the cost of the equipment. Equipment will be depreciated over its useful life by debiting the income statement account Depreciation Expense and crediting the balance sheet account Accumulated Depreciation (a contra asset account). These are both asset accounts and do not increase or decrease a company’s balance sheet.
Journal Entries for Prepaid Expenses
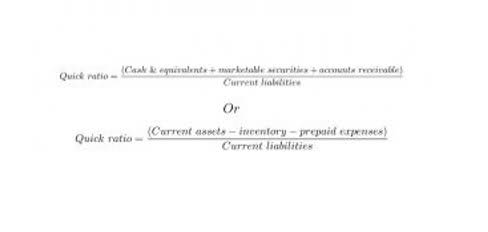
Interest paid in advance may arise as a company makes a payment ahead of the due date. Meanwhile, some companies pay taxes before they are due, such as an estimated tax payment based on what might come due in the future. Other less common prepaid expenses might include equipment rental or utilities. It adds the used amount to the expense account and reduces contra expense account the prepaid expense account to reflect the lower asset value. For a company, this monthly adjustment would be $2,000, which is $24,000 divided by 12 months. The quick ratio, while also being a liquidity ratio, only factors in an organization’s most liquid assets such as cash and cash equivalents that can be converted the quickest, hence the same.
Adjusting Entries – Asset Accounts

